AI Automation and the Future of Work: What’s Really Changing?
What if your job five years from now hasn’t been invented yet? Or what if your next teammate isn’t a person, but an algorithm?
Welcome to the world of AI automation and the future of work, where machines not only assist but sometimes think, analyze, and act. It’s a revolution that’s not coming—it’s already here.

This article explores how AI automation is transforming careers, reshaping industries, and creating both excitement and uncertainty in workplaces around the world.
Defining AI Automation: Beyond the Buzzword
AI automation combines artificial intelligence (AI) with automated processes to handle tasks that used to require human input. Unlike traditional automation, AI can learn, improve, and make decisions.

Think of:
- Chatbots answer customer questions.
- Algorithms scan resumes and shortlist candidates.
- Robots are assembling cars with precision.
- Predictive tools adjust marketing campaigns in real-time.
That’s AI automation at work.
A Brief History of Work and Technological Shifts

Work has always evolved with technology:
- The Industrial Revolution replaced manual labor with machines.
- The Digital Age introduced computers, making knowledge work faster.
- Now, AI automation is blending the two—digital power meets decision-making.
But unlike past changes, AI impacts both physical and cognitive tasks.
How AI Automation Is Reshaping Industries
From agriculture to accounting, industries are rethinking how work gets done.
AI in Action: From Manufacturing to Marketing
- Healthcare: AI assists in diagnostics, treatment plans, and administrative tasks.
- Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading are AI-driven.
- Retail: Personalized shopping, inventory optimization, and chatbots enhance user experience.
- Manufacturing: Robotics and predictive maintenance reduce downtime.
- Marketing: Tools like ChatGPT write copy, analyze sentiment, and A/B test content.
- Increased efficiency – Tasks completed faster and more accurately.
- 24/7 operations – Machines don’t sleep or take lunch breaks.
- Cost reduction – Less reliance on manual processes.
- Improved decision-making – AI turns data into actionable insights.
- Enhanced customer service – Instant, personalized responses.
AI automation and the future of work aren’t just about replacing effort—it’s about augmenting human capabilities.
Common Fears: Will AI Replace Human Jobs?
Let’s address the elephant in the room: job loss.
Yes, some jobs will disappear—especially those involving repetitive tasks. But history tells us that every tech shift also creates new roles. AI won’t eliminate work—it will redefine it.
The Human Element: Skills AI Can’t Replace
- Emotional intelligence
- Critical thinking
- Creativity
- Leadership
- Ethical judgment
Humans bring nuance, empathy, and context—things machines still struggle with.
AI Automation and the Rise of New Job Roles
Look around and you’ll find job titles that didn’t exist 10 years ago:
- AI ethicist
- Prompt engineer
- Data annotator
- Automation strategist
- Machine learning operations (MLOps) specialist
As AI automates old tasks, it also births entirely new career paths.
Education and Upskilling for the AI Era
To thrive in the AI-driven workplace, workers need to reskill and upskill.
- Digital literacy is a must.
- Data fluency helps understand AI outputs.
- Lifelong learning becomes the norm.
Platforms like Coursera, Udacity, and Khan Academy are already offering AI-related courses for every skill level.
How Companies Can Prepare for the Future of Work
Businesses must rethink workforce strategies:
- Invest in employee training
- Integrate AI tools ethically
- Redesign workflows for human-machine collaboration
- Encourage innovation, not just execution
The future belongs to companies that prepare today.
Remote Work, Gig Economy, and AI Synergy
AI and automation are powering the remote work revolution:
- Virtual assistants schedule meetings.
- AI monitors productivity metrics.
- Gig workers use platforms driven by smart matchmaking algorithms.
These trends are blurring the lines between employer, employee, and machine.
Ethical Questions Surrounding AI at Work
The rise of AI brings moral challenges:
- Should a bot be allowed to fire an employee?
- Can AI decision-making be fully trusted?
- How do we prevent bias in algorithms?
These are questions society must answer together.
AI, Inclusion, and Bias in Automation
AI is only as fair as the data it’s trained on. Poor data leads to biased outcomes. Ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI systems is critical to building a just future of work.
Government Policy and Labor Regulations in the AI Age
Governments worldwide are:
- Creating guidelines for ethical AI use
- Exploring universal basic income as a safety net
- Mandating transparency in automated decisions
Regulation must keep pace with innovation to protect workers.
Case Studies: Companies Leading AI-Driven Workforces
- Amazon uses AI for warehouse logistics and customer predictions.
- Google employs AI in search ranking and ad targeting.
- Netflix uses recommendation algorithms powered by machine learning.
- Siemens applies AI to optimize energy grids and manufacturing.
These companies are redefining workforces and inspiring others to follow.
Measuring Productivity in an AI-Augmented World
Traditional metrics like hours worked no longer fit. In the AI era, productivity is measured by:
- Output quality
- Speed to resolution
- Creative contribution
- Collaboration between humans and AI systems
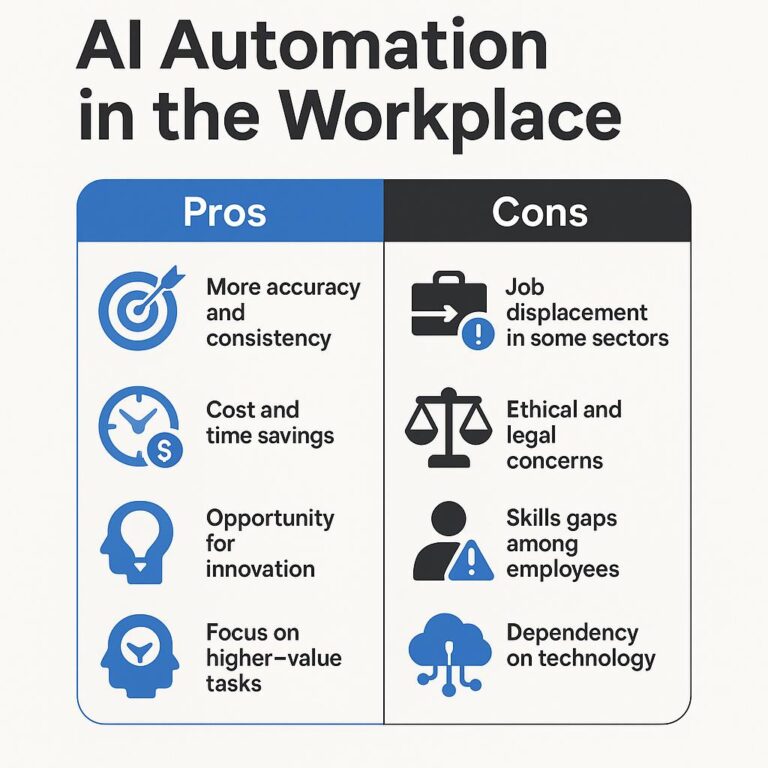
Pros and Cons of AI Automation in the Workplace
Pros:
- More accuracy and consistency
- Cost and time savings
- Opportunity for innovation
- Focus on higher-value tasks
Cons:
- Job displacement in some sectors
- Ethical and legal concerns
- Skills gaps among employees
- Dependency on technology
Predictions: What Will Work Look Like in 2030?

By 2030, we might see:
- AI mentors training junior employees
- Smart offices adapting to worker moods
- Job descriptions written by AI
- Global teams connected via real-time language translation
AI automation and the future of work is not science fiction—it’s a blueprint in progress.
Final Thoughts: Building a Human-Centered AI Future

We don’t need to fear the rise of the machines. We need to shape it.
A future where AI automates drudgery, humans focus on creativity, and both work in harmony is not just ideal—it’s achievable.
But it requires vision, responsibility, and a commitment to making people the center of progress.
FAQs – AI Automation and the Future of Work
1. What is AI automation, and how does it differ from traditional automation?
AI automation uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to perform tasks that go beyond simple rule-based automation. Traditional automation relies on fixed instructions, while AI can learn from data, adapt to new inputs, and make decisions with minimal human input. This means AI automation can handle unstructured tasks and improve over time.
2. Will AI automation eliminate jobs completely?
AI automation will transform jobs rather than eliminate them entirely. Some roles, especially those involving repetitive or manual tasks, may become obsolete. However, it will also create new roles in AI oversight, maintenance, ethics, and data science. The net effect depends on how individuals, organizations, and governments adapt to the transition.
3. What types of jobs are most at risk due to AI automation?
Jobs that involve routine, predictable tasks—like data entry, basic customer service, and some aspects of manufacturing—are more vulnerable to automation. However, even these roles can evolve, with humans overseeing AI systems and focusing on exceptions and complex cases.
4. What skills will be most valuable in an AI-driven workplace?
Soft skills like communication, emotional intelligence, critical thinking, and creativity will remain in demand. In addition, digital literacy, data analysis, and adaptability will be crucial. The ability to work effectively alongside AI tools will define many future career paths.
5. How can individuals prepare for careers in the AI era?
Lifelong learning is key. Professionals should seek online courses, certifications, and hands-on experience in areas like data science, AI ethics, programming, and automation tools. Understanding how AI works, even at a basic level, is increasingly important across all sectors.
6. Is AI automation only relevant to tech companies?
No. AI automation is impacting every industry—from healthcare and agriculture to law, education, and finance. Even small businesses are using AI tools to improve efficiency, customer engagement, and decision-making.
7. How will AI affect workplace culture?
AI may reduce micromanagement and increase productivity by taking over repetitive tasks. This could free employees to focus on meaningful work, fostering creativity and innovation. However, it may also create anxiety if not introduced transparently. Open communication and training are essential.
8. What role does ethics play in AI automation?
Ethics is critical. Decisions made by AI systems must be fair, transparent, and accountable. Bias in AI models, lack of transparency, and unjust outcomes can lead to discrimination. Ethical frameworks and responsible governance are essential to ensure trust in AI-driven workplaces.
9. Are there jobs that AI will never be able to do?
Jobs that require deep human empathy, cultural understanding, moral reasoning, or unpredictable decision-making are unlikely to be fully automated. For example, therapists, artists, teachers, and leaders in human development will remain rooted in human interaction.
10. How does AI impact employee performance measurement?
Traditional performance metrics may become outdated. AI allows for more nuanced tracking of productivity, collaboration, and outcomes. However, companies must balance data-driven insights with privacy, fairness, and contextual understanding.
11. Can AI help reduce workplace bias?
When designed and used responsibly, AI can help eliminate unconscious human biases—such as in recruitment or performance reviews. However, if trained on biased data, AI can reinforce discrimination. Continuous auditing and diverse data sets are essential.
12. How does AI support remote and hybrid work models?
AI tools support remote work by automating scheduling, tracking productivity, summarizing meetings, and analyzing communication patterns. They can also power virtual assistants and help remote teams stay connected and efficient across time zones.
13. What’s the difference between AI augmentation and AI replacement?
AI augmentation refers to AI tools supporting human work, making it faster or easier. AI replacement refers to systems that completely take over tasks from humans. Most AI in today’s workplaces falls under augmentation, enhancing—not replacing—human roles.
14. What is “human-centered AI,” and why is it important?
Human-centered AI prioritizes human values, collaboration, and well-being in the design and deployment of AI systems. It ensures technology serves people rather than controls them. In the future of work, it’s vital to keep empathy, ethics, and human dignity at the forefront.
15. What is the gig economy’s relationship with AI automation?
AI powers many platforms in the gig economy by matching freelancers with tasks, setting dynamic pricing, and evaluating quality. At the same time, it helps automate background tasks that enable gig workers to focus on service delivery. It creates more flexible but also more algorithm-driven work environments.
16. Can AI automation help reduce burnout and improve mental health at work?
Yes, if applied thoughtfully. AI can take over tedious tasks, reduce workload, and alert managers to signs of burnout through behavioral data. However, excessive monitoring or a lack of human interaction may increase stress. Balance is essential.
17. How can businesses adopt AI without alienating employees?
By being transparent, inclusive, and supportive. Involve employees in the process, offer upskilling opportunities, and emphasize that AI is a tool to support—not replace—them. Change management and communication are key to a smooth transition.
18. Will AI affect executive and leadership roles too?
Yes. AI can support decision-making by offering insights from vast datasets. Leaders will need to become AI-literate to make informed strategic choices. Emotional intelligence, vision, and ethical responsibility will remain core human traits in leadership.
19. How will the education system evolve to prepare future workers?
Yes. AI can support decision-making by offering insights from vast datasets. Leaders will need to become AI-literate to make informed strategic choices. Emotional intelligence, vision, and ethical responsibility will remain core human traits in leadership.
20. What does the workplace of 2030 look like with AI?
It’s a hybrid of human and machine collaboration. Offices may be powered by smart assistants, predictive analytics, and virtual collaboration spaces. Teams will include both humans and AI agents, working seamlessly to create, solve, and innovate. Flexibility, adaptability, and empathy will define the most successful workplaces.